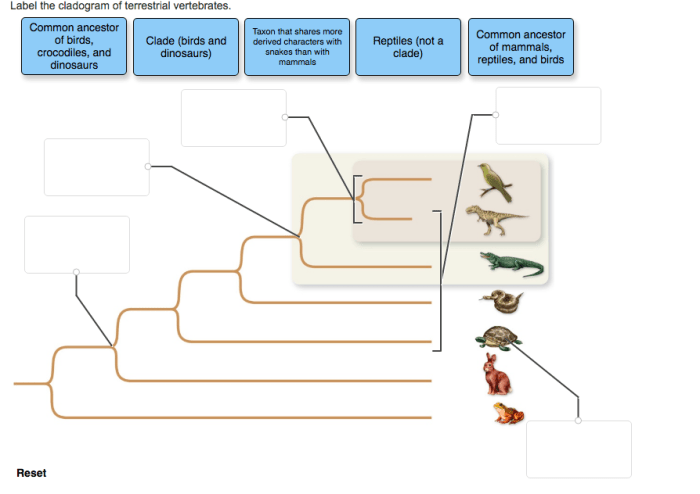
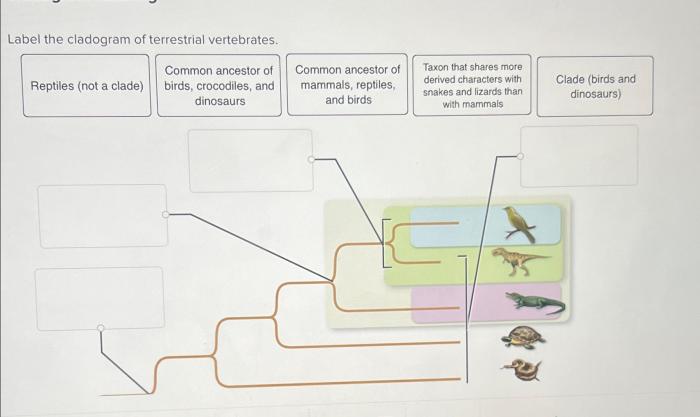
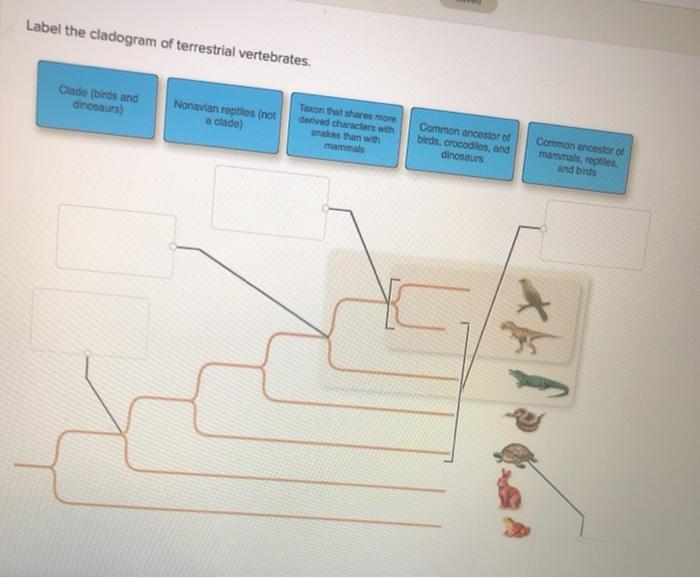
Label the cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates. – Label the cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This captivating journey will delve into the intricate web of evolutionary relationships among terrestrial vertebrates, unraveling the secrets of their diversification and adaptation.
The cladogram, a powerful tool in evolutionary biology, serves as a roadmap guiding us through the evolutionary history of these fascinating creatures. By meticulously labeling this cladogram, we gain invaluable insights into the hierarchical organization of terrestrial vertebrates, the synapomorphies that define each clade, and the homoplasies that challenge our understanding of their evolutionary relationships.
Cladogram of Terrestrial Vertebrates
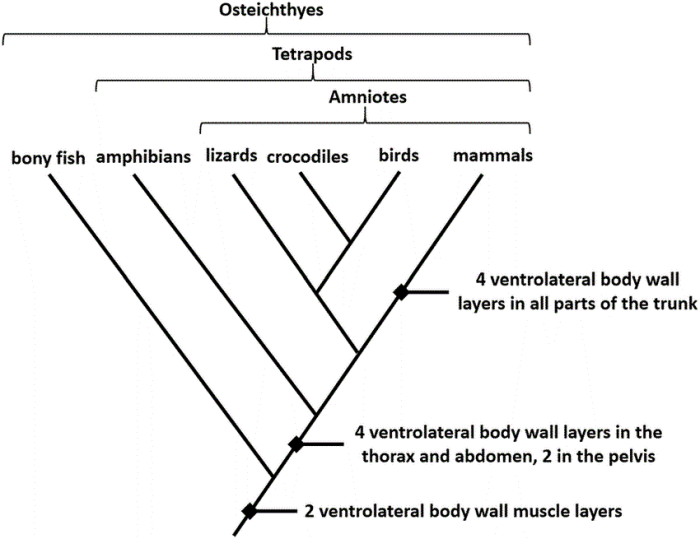
A cladogram is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms. The cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates shows the relationships among the major groups of vertebrates that live on land. The cladogram is based on the principle of common descent, which states that all organisms are descended from a common ancestor.
The cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates is organized hierarchically. The most inclusive group is the Tetrapoda, which includes all vertebrates that have four limbs. The Tetrapoda are divided into two main groups, the Amphibia and the Amniota. The Amphibia are the most primitive group of terrestrial vertebrates, and they include frogs, salamanders, and caecilians.
The Amniota are the more advanced group of terrestrial vertebrates, and they include reptiles, birds, and mammals.
The cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates shows the evolutionary relationships among the major groups of vertebrates that live on land. The cladogram is based on the principle of common descent, which states that all organisms are descended from a common ancestor.
Labeling the Cladogram, Label the cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates.
The cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates can be labeled with the taxonomic groups and clade names. The taxonomic groups are the groups of organisms that are represented on the cladogram. The clade names are the names of the branches on the cladogram.
The clades are the groups of organisms that are descended from a common ancestor.
The criteria used for assigning labels to the clades are the synapomorphies. Synapomorphies are shared derived characters that are unique to a particular group of organisms. The synapomorphies that define each clade on the cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates are:
- Tetrapoda: four limbs
- Amniota: amniotic egg
- Reptilia: scales
- Aves: feathers
- Mammalia: hair
Synapomorphies and Homoplasies
Synapomorphies are shared derived characters that are unique to a particular group of organisms. Homoplasies are characters that are similar in two or more groups of organisms but are not shared derived characters. Homoplasies can be the result of convergent evolution, which is the evolution of similar characters in two or more groups of organisms that are not closely related.
Synapomorphies and homoplasies can be used to support or refute hypotheses about vertebrate evolution. Synapomorphies provide evidence for the common ancestry of a group of organisms. Homoplasies can provide evidence for convergent evolution.
Major Clades of Terrestrial Vertebrates
The major clades of terrestrial vertebrates are the Tetrapoda, Amphibia, Amniota, Reptilia, Aves, and Mammalia.
- Tetrapoda: four limbs
- Amphibia: frogs, salamanders, and caecilians
- Amniota: reptiles, birds, and mammals
- Reptilia: scales
- Aves: feathers
- Mammalia: hair
The major clades of terrestrial vertebrates have evolved a variety of adaptations that have enabled them to thrive in terrestrial environments. These adaptations include the development of limbs, the evolution of the amniotic egg, and the development of hair.
Phylogenetic Relationships
The cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates supports the traditional classification of vertebrates. The cladogram shows that the Tetrapoda are the most primitive group of terrestrial vertebrates, and that the Amphibia are the most primitive group of Amniota. The cladogram also shows that the Reptilia, Aves, and Mammalia are the most closely related groups of terrestrial vertebrates.
The cladogram of terrestrial vertebrates has implications for our understanding of vertebrate evolution. The cladogram shows that the major groups of terrestrial vertebrates have evolved from a common ancestor. The cladogram also shows that the evolution of terrestrial vertebrates has been a complex process, and that the major groups of terrestrial vertebrates have evolved a variety of adaptations that have enabled them to thrive in terrestrial environments.
Questions Often Asked: Label The Cladogram Of Terrestrial Vertebrates.
What is a cladogram?
A cladogram is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms, based on shared characteristics.
What are synapomorphies?
Synapomorphies are shared derived characters that define a clade, indicating a common ancestor.
What is the significance of homoplasies?
Homoplasies are similar characteristics that arise independently in different lineages, potentially obscuring evolutionary relationships.