Label the parts of the prokaryotic cell, the building blocks of life, and embark on a journey into the microscopic realm. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricate structures and functions of prokaryotic cells, providing a foundation for understanding the fundamentals of biology.
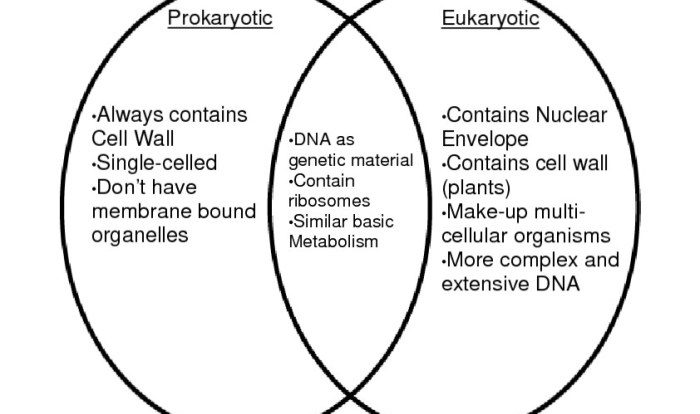
Prokaryotic cells, the simplest and most ancient form of life, play a pivotal role in the Earth’s ecosystems. They are essential for nutrient cycling, decomposition, and even human health. By understanding the components of prokaryotic cells, we gain insights into the origins of life and the diversity of the microbial world.
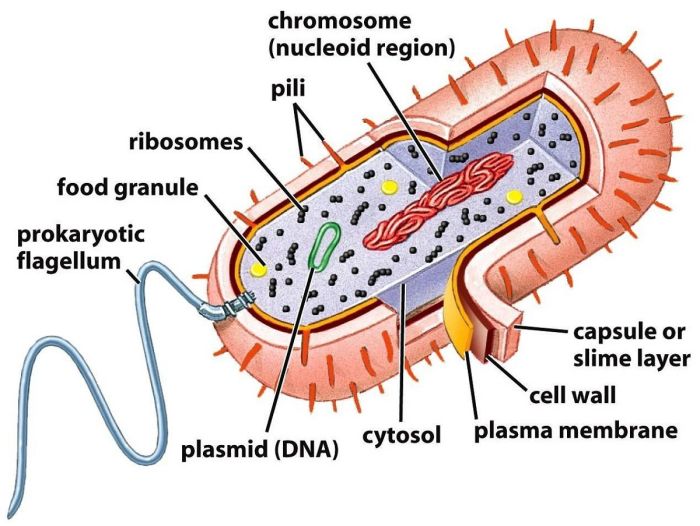
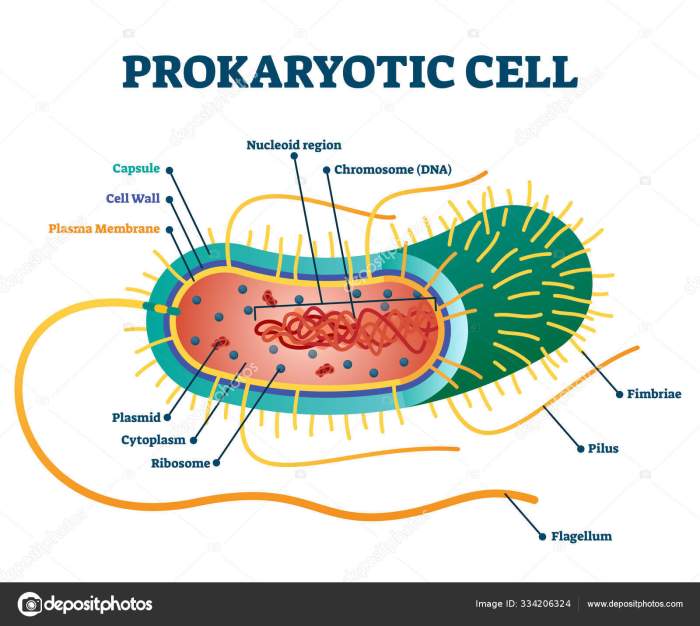
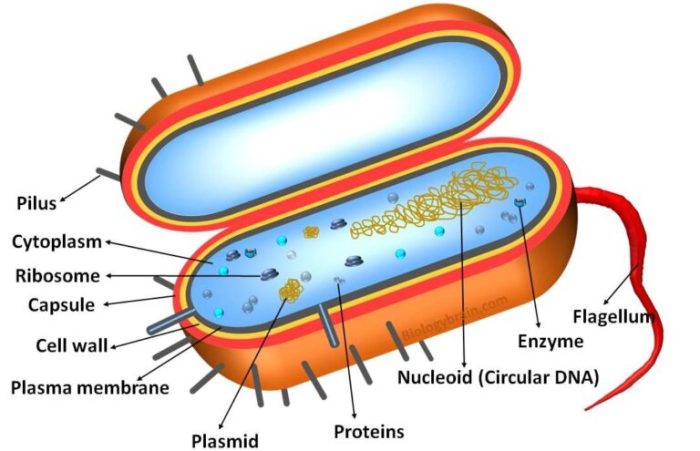
Major Parts of a Prokaryotic Cell: Label The Parts Of The Prokaryotic Cell
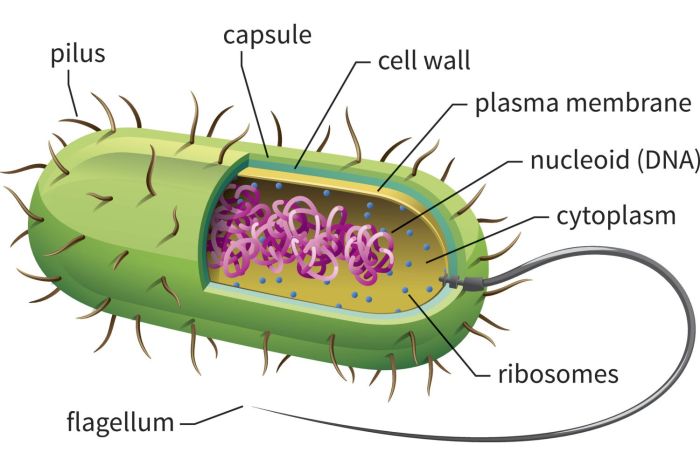
Prokaryotic cells are simple, single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. They are found in a wide variety of habitats, including soil, water, and the human body. Prokaryotic cells are essential for the cycling of nutrients in the environment and for the production of oxygen.Labeling
the parts of a prokaryotic cell is important for understanding its structure and function. The major parts of a prokaryotic cell include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and nucleoid region.
Cell Membrane, Label the parts of the prokaryotic cell
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer that surrounds the cell. It protects the cell from its surroundings and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which is a double layer of phospholipids.
Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail. The hydrophilic heads face outward, toward the water-based environment, while the hydrophobic tails face inward, away from the water.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell. It contains all of the cell’s organelles, which are small structures that perform specific functions. The cytoplasm is also the site of many of the cell’s metabolic reactions.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small, round organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis. They are composed of RNA and protein. Ribosomes bind to mRNA molecules and translate the genetic code into a sequence of amino acids.
Nucleoid Region
The nucleoid region is the area of the cell that contains the cell’s DNA. The DNA is organized into a single, circular chromosome. The nucleoid region is not surrounded by a membrane, which is one of the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Top FAQs
What is the function of the cell membrane in prokaryotic cells?
The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell, maintaining its internal environment and protecting it from external threats.
What is the role of ribosomes in prokaryotic cells?
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, the process by which cells create the proteins they need to function.
What is the significance of the nucleoid region in prokaryotic cells?
The nucleoid region contains the cell’s genetic material, DNA, which carries the instructions for all cellular activities.