Chapter 6 Polygons and Quadrilaterals Answer Key unlocks a treasure trove of knowledge, providing an authoritative and comprehensive exploration of these geometric shapes. This definitive resource empowers readers with a profound understanding of the characteristics, properties, and applications of polygons and quadrilaterals, equipping them with the tools to navigate the complexities of geometry with confidence.
Delving into the intricacies of polygons and quadrilaterals, this guide unravels their defining features, enabling readers to distinguish between different types with ease. Through insightful explanations and illustrative examples, it illuminates the properties that govern these shapes, including their number of sides, angles, and diagonals.
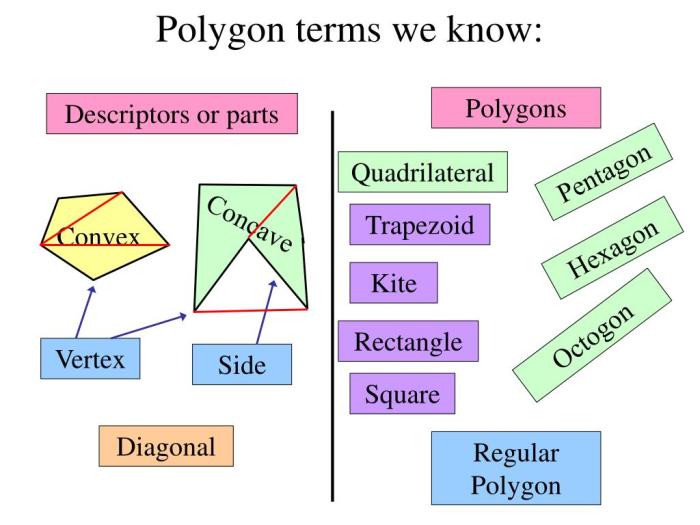
Polygons and Quadrilaterals
In geometry, a polygon is a two-dimensional shape with straight sides. A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides. Polygons and quadrilaterals are fundamental shapes used in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and art.
Characteristics of Polygons
- Number of sides: Polygons can have any number of sides, from three to infinity.
- Angles: The angles of a polygon are the measures of the angles formed by the intersection of its sides.
- Diagonals: Diagonals are line segments that connect non-adjacent vertices of a polygon.
Characteristics of Quadrilaterals
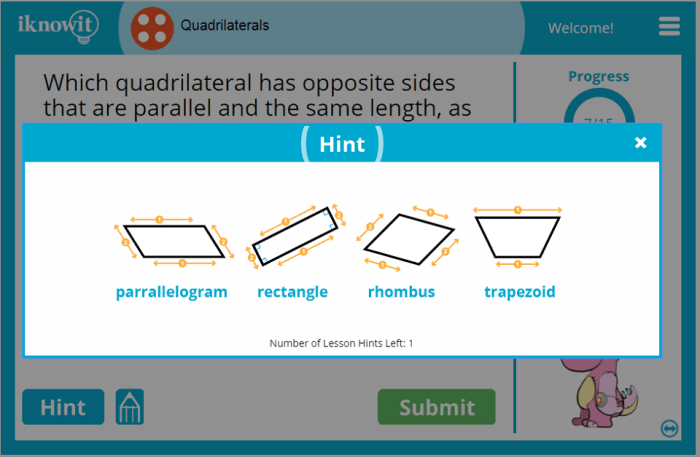
- Types of sides: Quadrilaterals can have four equal sides (rhombus), four unequal sides (quadrilateral), two pairs of equal sides (parallelogram), or no equal sides (trapezoid).
- Angles: Quadrilaterals can have four right angles (rectangle), four acute angles (rhombus), two acute angles and two obtuse angles (trapezoid), or four obtuse angles (concave quadrilateral).
- Diagonals: Quadrilaterals can have two diagonals that bisect each other (rectangle, rhombus, square), or two diagonals that do not bisect each other (parallelogram, trapezoid).
Properties of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
- Interior angle sum: The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is (n-2) x 180 degrees.
- Exterior angle sum: The sum of the exterior angles of a polygon is always 360 degrees.
- Area: The area of a polygon can be calculated using various formulas, depending on the shape of the polygon.
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
Classifying Polygons and Quadrilaterals, Chapter 6 polygons and quadrilaterals answer key
Polygons can be classified based on the number of sides, such as triangles (3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), hexagons (6 sides), and so on.
Quadrilaterals can be classified based on the length of sides and angles, such as squares (4 equal sides, 4 right angles), rectangles (4 right angles), parallelograms (2 pairs of equal sides), trapezoids (1 pair of parallel sides), and rhombuses (4 equal sides).
Applications of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
- Architecture: Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Engineering: Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in the design of machines, vehicles, and other mechanical devices.
- Art: Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in paintings, sculptures, and other forms of art.
FAQ: Chapter 6 Polygons And Quadrilaterals Answer Key
What is the difference between a polygon and a quadrilateral?
A polygon is any closed figure with three or more straight sides, while a quadrilateral is a polygon with specifically four sides.
How can I calculate the area of a rectangle?
To calculate the area of a rectangle, multiply its length by its width: Area = Length × Width.
What are the different types of quadrilaterals?
There are various types of quadrilaterals, including squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and rhombuses.